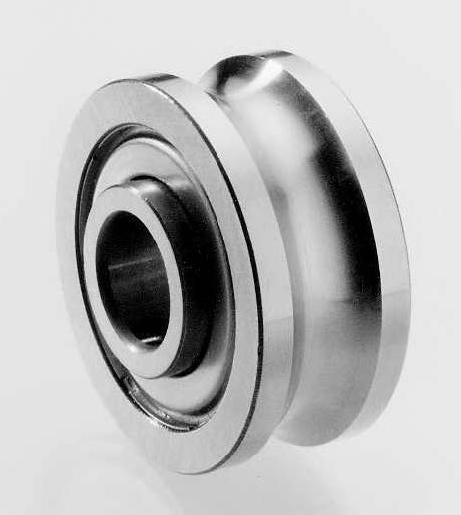
Product Description
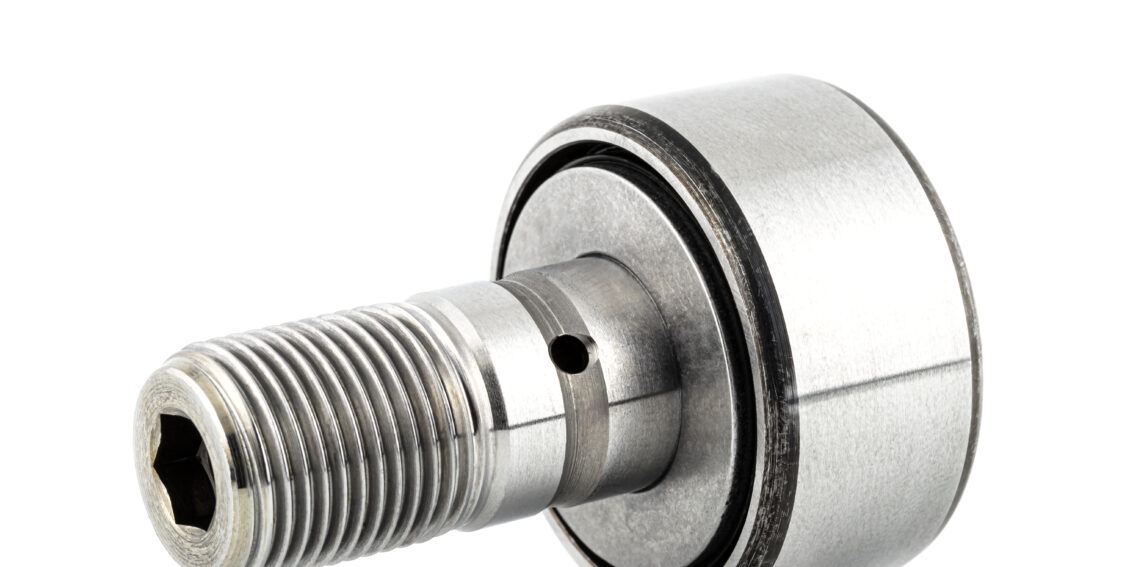
Line Track Rollers Bearing W1 W1X RM1 RM1 2RS for sliding CZPT rail
W series RM series V groove bearing size:
|
Designation
|
A1 | A2 | Chamfer r/min | Weight | ||||||
| Bore | O.D. | Width | mm | Load | ||||||
| mm | mm | mm | ||||||||
| D1 | D | B | A1 | A2 | R/min | Cw(KN) | Cow(KN) | Kg | ||
| W1 | 4.763 | 19.56 | 7.87 | 7.9. | 11.86 | 0.3 | 2.2 | 1 | 11 | |
| W1X | 4.763 | 19.56 | 7.87 | 7.93 | 11.86 | 0.3 | 2.2 | 1 | 11 | |
| W2 | 9.525 | 30.73 | 11.1 | 12.7 | 18.24 | 0.3 | 4.9 | 2.5 | 38 | |
| W2X | 9.525 | 30.73 | 11.1 | 12.7 | 18.24 | 0.3 | 4.9 | 2.5 | 38 | |
| W3 | 12 | 45.72 | 15.88 | 19.05 | 26.98 | 0.6 | 9.4 | 4.9 | 130 | |
| W3X | 12 | 45.72 | 15.88 | 19.05 | 26.98 | 0.6 | 9.4 | 4.9 | 130 | |
| W4 | 15 | 59.94 | 19.05 | 25.4 | 34.93 | 1 | 14.8 | 8.2 | 280 | |
| W4X | 15 | 59.94 | 19.05 | 25.4 | 34.93 | 1 | 14.8 | 8.2 | 280 | |
| RM1ZZ | 4.763 | 19.56 | 7.87 | 7.9. | 11.86 | 0.3 | 2.2 | 1 | 11 | |
| RM1 2RS | 4.763 | 19.56 | 7.87 | 7.93 | 11.86 | 0.3 | 2.2 | 1 | 11 | |
| RM2ZZ | 9.525 | 30.73 | 11.1 | 12.7 | 18.24 | 0.3 | 4.9 | 2.5 | 38 | |
| RM2 2RS | 9.525 | 30.73 | 11.1 | 12.7 | 18.24 | 0.3 | 4.9 | 2.5 | 38 | |
| RM3ZZ | 12 | 45.72 | 15.88 | 19.05 | 26.98 | 0.6 | 9.4 | 4.9 | 130 | |
| RM3 2RS | 12 | 45.72 | 15.88 | 19.05 | 26.98 | 0.6 | 9.4 | 4.9 | 130 | |
| RM4ZZ | 15 | 59.94 | 19.05 | 25.4 | 34.93 | 1 | 14.8 | 8.2 | 280 | |
| RM4 2RS | 15 | 59.94 | 19.05 | 25.4 | 34.93 | 1 | 14.8 | 8.2 | 280 | |
Specifications
1. Cheap and high quality bearing
2. OEM service offered
3. Low noise, long life
4. Ease of assembly
5. Stock available
Our company are specialized in manufacturing various types of bearings and we also accept OEM service with CZPT CZPT CZPT NTN NMB etc brand.
We can produce the bearings accordingly to the customers’ Samples or Drawings.
Any need,please kindly contact us
Ivy wang
Packaging & Delivery
A. According to customer’s requirements.
B.The outer is color polybag + box + carton, industrial standard packaging.
Delivery Detail: 1-3 working days after order confirmed. (depend on the amount)
Application
For mounting wherever axial and radial loads are expected
For most parts for torque transmission
Home appliances, electric motors, automotive components
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Rolling Body: | Roller Bearings |
|---|---|
| The Number of Rows: | Double |
| Outer Dimension: | 10-60mm |
| Material: | Bearing Steel |
| Spherical: | Non-Aligning Bearings |
| Load Direction: | Radial Bearing |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
How does proper installation and alignment impact the performance and longevity of track bearings?
Proper installation and alignment play a critical role in the performance and longevity of track bearings. Correct installation ensures that the bearings are positioned and secured accurately, while proper alignment ensures that the load is distributed evenly and the bearings operate smoothly. Here’s an explanation of how proper installation and alignment impact the performance and longevity of track bearings:
Installation Impact:
- Load Distribution: Proper installation ensures that the track bearings are aligned and positioned correctly, allowing for even load distribution. When bearings are installed incorrectly, the load may be unevenly distributed, leading to excessive wear on certain parts of the bearings and reduced overall performance.
- Stability and Rigidity: Accurate installation provides stability and rigidity to the track bearings. Properly secured bearings minimize the risk of movement or vibration during operation, which can cause additional stress, premature wear, and potential damage to the bearings and surrounding components.
- Reduction of Misalignment: Correct installation minimizes the chances of misalignment between the track bearings and the track or guide rails. Misalignment can lead to uneven loading, increased friction, and accelerated wear and tear on the bearings. Proper alignment reduces these issues, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
- Prevention of Contamination: During installation, it is important to take precautions to prevent contamination of the track bearings. Proper handling techniques, cleanliness, and the use of appropriate tools or protective measures help avoid introducing dirt, dust, or debris that can compromise the bearing’s performance and longevity.
Alignment Impact:
- Reduced Friction and Wear: Proper alignment of track bearings helps minimize friction and wear. When bearings are misaligned, excessive forces and irregular motion can occur, leading to increased friction and accelerated wear. Proper alignment ensures that the bearings operate within their intended design parameters, reducing friction and promoting longevity.
- Optimal Load Distribution: Correct alignment ensures that the load is distributed evenly across the track bearings. This prevents excessive stress on specific areas of the bearings, reducing the risk of premature failure and extending their service life. Optimal load distribution also contributes to smoother operation and improved overall performance.
- Minimized Noise and Vibration: Proper alignment helps minimize noise and vibration during operation. Misaligned track bearings can result in irregular motion, leading to unwanted noise and vibration that can affect the performance, comfort, and efficiency of the machinery or equipment. Proper alignment promotes smoother and quieter operation.
- Improved Efficiency: When track bearings are correctly aligned, the machinery or equipment experiences reduced resistance and improved efficiency. Misalignment can result in energy losses, increased power consumption, and decreased overall efficiency. Proper alignment ensures optimal power transfer and minimizes energy wastage.
It is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the specific track bearings being installed. Proper installation techniques, including accurate positioning, secure fastening, and appropriate alignment, contribute to the optimal performance, reliability, and longevity of track bearings in various applications.

Are there potential challenges or limitations in using track bearings in specific industries?
While track bearings are widely used in various industries for their ability to support linear motion and handle heavy loads, there can be potential challenges and limitations associated with their use in specific industries. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Contamination and Harsh Environments:
Industries such as mining, construction, and agriculture often operate in harsh environments with high levels of contamination, including dust, dirt, and moisture. These contaminants can enter the track bearings and cause accelerated wear, reduced performance, and potential failure. Regular maintenance and appropriate sealing measures are required to mitigate these challenges.
2. High-Temperature Environments:
In industries like metal processing, glass manufacturing, and foundries, track bearings may be exposed to high temperatures. Excessive heat can affect the lubrication properties and structural integrity of bearings, leading to premature failure. Selecting track bearings specifically designed for high-temperature applications and using suitable lubricants are necessary to overcome this limitation.
3. Corrosive Chemicals:
Industries such as chemical processing, food and beverage, and wastewater treatment involve exposure to corrosive chemicals. Corrosion can significantly affect the performance and lifespan of track bearings. Choosing bearings made from corrosion-resistant materials or applying protective coatings can help address this challenge.
4. Heavy Load and Impact:
Industries like material handling, mining, and construction often require track bearings to withstand heavy loads and frequent impacts. Excessive load or impact can lead to premature wear, deformation, or even catastrophic failure of the bearings. Selecting track bearings with appropriate load capacities and impact resistance is crucial in these industries.
5. Precision and Accuracy:
In industries such as robotics, semiconductor manufacturing, and precision machining, track bearings may need to meet stringent requirements for precision and accuracy. Any deviation or play in the bearings can impact the overall performance and quality of the process. Using high-precision track bearings and ensuring proper alignment and installation are essential in these cases.
6. Speed and Acceleration:
Applications involving high-speed or rapid acceleration, such as automated assembly lines or conveyor systems, can impose additional challenges on track bearings. Excessive speed or acceleration can generate heat and vibration, leading to increased wear and reduced bearing life. Choosing track bearings with suitable speed and acceleration ratings is vital in these industries.
It is important to consult with bearing manufacturers or industry experts to identify and address any potential challenges or limitations specific to the industry and application at hand. By understanding these challenges and selecting track bearings designed to overcome them, industries can optimize performance, reliability, and longevity while mitigating risks and ensuring smooth operation.

How do track bearings compare to other types of bearings like ball bearings or roller bearings?
Track bearings, ball bearings, and roller bearings are all types of rolling bearings used in various applications. Let’s compare track bearings to ball bearings and roller bearings to understand their similarities and differences:
- Design and Construction: Track bearings, ball bearings, and roller bearings have different designs and constructions. Track bearings, also known as track rollers or track follower bearings, are designed specifically for guided linear or rotational motion along a track or guide rail. They feature an outer ring with a track surface, an inner ring, rolling elements (such as rollers or needles), and a cage. Ball bearings, on the other hand, have spherical rolling elements (balls) sandwiched between inner and outer rings. Roller bearings, as the name suggests, have cylindrical or tapered rolling elements (rollers) between inner and outer rings.
- Motion and Load Handling: Track bearings are primarily used for guided motion in track-based systems, while ball bearings and roller bearings are used for general rotational or linear motion. Track bearings are designed to support both radial and axial loads and provide smooth and controlled motion along the track. Ball bearings and roller bearings are also capable of supporting radial and axial loads but are typically used in applications where the motion is not constrained to a specific track or guide rail. Roller bearings, with their larger contact area and higher load-carrying capacity, are often preferred for applications with higher loads.
- Applications: Track bearings are commonly used in applications such as material handling systems, conveyors, cam mechanisms, automated machinery, construction equipment, and agricultural machinery, where guided motion along a track or rail is required. Ball bearings and roller bearings find applications in a wide range of industries and systems, including electric motors, pumps, automotive applications, industrial machinery, and appliances.
- Friction and Efficiency: Track bearings, ball bearings, and roller bearings all aim to minimize friction and ensure efficient operation. However, due to their different designs and contact surfaces, they exhibit varying levels of friction. Ball bearings typically have lower friction due to point contact between the balls and the raceways. Roller bearings, especially tapered roller bearings, distribute the load over a larger contact area, resulting in slightly higher friction compared to ball bearings. Track bearings, with their track interface, may have slightly higher friction compared to ball bearings or roller bearings due to the rolling elements’ contact with the track surface.
- Installation and Maintenance: Track bearings, ball bearings, and roller bearings require proper installation and maintenance for optimal performance and longevity. However, track bearings may require additional attention during installation as they need to be properly aligned with the track or guide rail. Regular lubrication and periodic inspection are essential for all types of bearings to ensure smooth operation and prevent premature failure.
In summary, track bearings, ball bearings, and roller bearings have distinct designs and applications. Track bearings are specialized for guided motion along a track or rail, while ball bearings and roller bearings are more versatile and used in a wide range of rotational or linear motion applications. Each type of bearing has its advantages and considerations in terms of load handling, friction, efficiency, and installation requirements. Selecting the appropriate bearing type depends on the specific application requirements, load conditions, motion characteristics, and environmental factors.


editor by CX 2024-04-16