Product Description
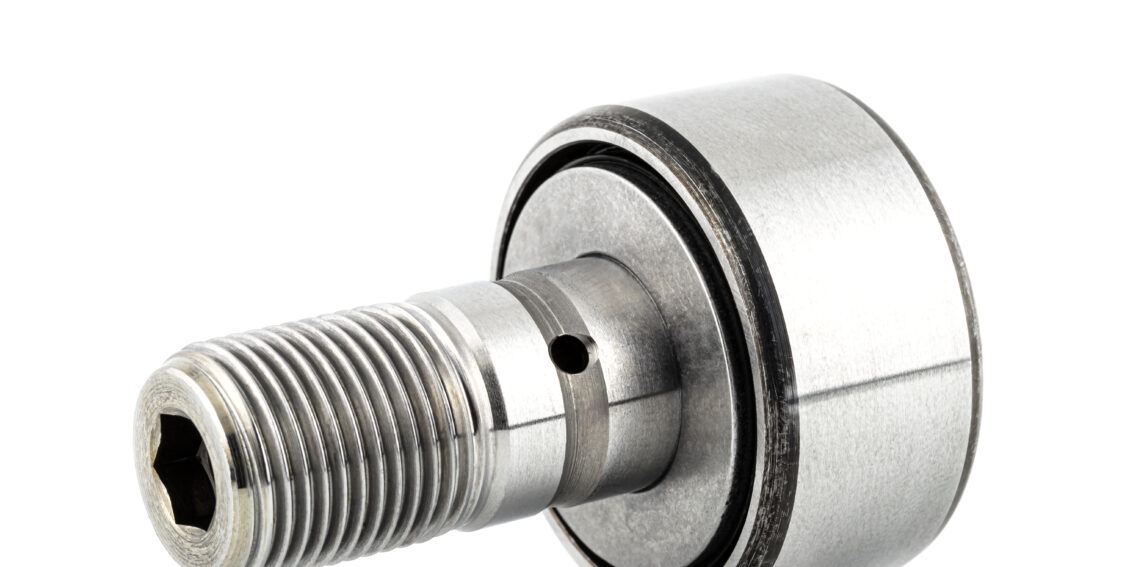
High Quality CF/KR/CFFR Series Track Roller Cam Follower Bearing
Description of High Quality CF/KR/CFFR Series Track Roller Cam Follower Bearing
| Series | Description |
| NATR | Yoke type track rollers with axial guidance by washers,gap seal,with inner ring |
| NATR…PP | Yoke type track rollers with additional sealing rings |
| NATV | Yoke type track rollers with axial guidance by washers,full complement,gap seal,with inner ring |
| NATV…PP | Yoke type track rollers with additional sealing rings |
| NUTR | Yoke type track rollers with axial guidance by the rolling element,full complement,gap seal,with inner ring |
| KR | Stud type track rollers with axial guidance by rid and washer,gap seal |
| KR…PP | Stud type track rollers with sealing rings |
| KRE | Stud type track rollers with eccentric collar |
| KRE…PP | Stud type track rollers with eccentric collar and sealing rings |
| KRV | Stud type track rollers with axial guidance by rid and washer,full complement, gap seal |
| KRV…PP | Stud type track rollers with sealing rings |
| KRVE | Stud type track rollers with eccentric collar |
| KRVE…PP | Stud type track rollers with eccentric collar and sealing rings |
| NUKR | Stud type track rollers with axial guidance by the rolling element,full complement, gap seals |
| NUKRE | Stud type track rollers with eccentric collar |
| CF | Stud type track rollers with cage ,the same as KR series |
Catalogue of High Quality CF/KR/CFFR Series Track Roller Cam Follower Bearing
|
Outside Diameter |
Bearing Designation and mass approx | Borndary Dimensions | ||||||||||||||
|
Without Eccentric Collar |
Mass |
With Ecctric Coollar |
Mass | D | d | C | B | B1 | B2 | G | G1 | M | M1 | C1 | d2 | |
| mm | g | g | mm | |||||||||||||
| 47 | KR 47 | 386 | KRE 47 | 405.5 | 47 | 20 | 24 | 66 | 40.5 | 9 | M20×1.5 | 21 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 37 |
| KR 47 PP | 386 | KRE 47 PP | 405.5 | 47 | 20 | 24 | 66 | 40.5 | 9 | M20×1.5 | 21 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 37 | |
| KRV 47 | 390 | KRVE 47 | 409.5 | 47 | 20 | 24 | 66 | 40.5 | 9 | M20×1.5 | 21 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 37 | |
| KRV 47 PP | 390 | KRVE 47 PP | 409.5 | 47 | 20 | 24 | 66 | 40.5 | 9 | M20×1.5 | 21 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 37 | |
| NUKR 47 | 380 | NUKPE 47 | 399.5 | 47 | 20 | 24 | 66 | 40.5 | 9 | M20×1.5 | 21 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 27 | |
| 52 | KR 52 | 461 | KRE 40 | 480.5 | 52 | 20 | 24 | 66 | 40.5 | 9 | M20×1.5 | 21 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 37 |
| KR 52 PP | 461 | KRE 52 PP | 480.5 | 52 | 20 | 24 | 66 | 40.5 | 9 | M20×1.5 | 21 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 37 | |
| KRV 52 | 465 | KRVE 52 | 484.5 | 52 | 20 | 24 | 66 | 40.5 | 9 | M20×1.5 | 21 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 37 | |
| KRV 52 PP | 465 | KRVE 52 PP | 484.5 | 52 | 20 | 24 | 66 | 40.5 | 9 | M20×1.5 | 21 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 37 | |
| NUKR 52 | 450 | NUKPE 52 | 469.5 | 52 | 20 | 24 | 66 | 49.5 | 9 | M20×1.5 | 21 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 31 | |
| 62 | KR 62 | 790 | KRE 62 | 818.2 | 62 | 24 | 29 | 80 | 49.5 | 11 | M24×1.5 | 25 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 44 |
| KR 62 PP | 790 | KRE 62 PP | 818.2 | 62 | 24 | 29 | 80 | 49.5 | 11 | M24×1.5 | 25 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 44 | |
| KRV 62 | 802 | KRVE 62 | 830.2 | 62 | 24 | 29 | 80 | 49.5 | 11 | M24×1.5 | 25 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 44 | |
| KRV 62 PP | 802 | KRVE 62 PP | 830.2 | 62 | 24 | 29 | 80 | 49.5 | 11 | M24×1.5 | 25 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 44 | |
| NUKR 62 | 795 | NUKPE 62 | 823.5 | 62 | 24 | 29 | 80 | 49.5 | 11 | M24×1.5 | 25 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 38 | |
| 72 | KR 72 | 1040 | KRE 72 | 1068.2 | 72 | 24 | 29 | 80 | 49.5 | 11 | M20×1.5 | 25 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 44 |
| KR 72 PP | 1040 | KRE 72 PP | 1068.2 | 72 | 24 | 29 | 80 | 49.5 | 11 | M24×1.5 | 25 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 44 | |
| KRV 72 | 1045 | KRVE 72 | 1073.2 | 72 | 24 | 29 | 80 | 49.5 | 11 | M24×1.5 | 25 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 44 | |
| KRV 72 PP | 1045 | KRVE 72 PP | 1073.2 | 72 | 24 | 29 | 80 | 49.5 | 11 | M24×1.5 | 25 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 44 | |
| NUKR 72 | 1200 | NUKPE 72 | 1038.2 | 72 | 24 | 29 | 80 | 49.5 | 11 | M24×1.5 | 25 | 8 | 4 | 0.8 | 44 | |
| 80 | KR 80 | 1550 | KRE 80 | 1610 | 80 | 30 | 35 | 100 | 63 | 15 | M30×1.5 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 53 |
| KR 80 PP | 1550 | KRE 80 PP | 1610 | 80 | 30 | 35 | 100 | 63 | 15 | M30×1.5 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 53 | |
| KRV 80 | 1561 | KRVE 80 | 1621 | 80 | 30 | 35 | 100 | 63 | 15 | M30×1.5 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 53 | |
| KRV 80 PP | 1561 | KRVE 80 PP | 1621 | 80 | 30 | 35 | 100 | 63 | 15 | M30×1.5 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 53 | |
| NUKR 80 | 1800 | NUKPE 80 | 1600 | 80 | 30 | 35 | 100 | 63 | 15 | M30×1.5 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 47 | |
| 85 | KR 85 | 1740 | KRE 85 | 1800 | 85 | 30 | 35 | 100 | 63 | 15 | M30×1.5 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 53 |
| KR 85 PP | 1740 | KRE 85 PP | 1800 | 85 | 30 | 35 | 100 | 63 | 15 | M30×1.5 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 53 | |
| 90 | KR 90 | 1950 | KRE 90 | 2571 | 90 | 30 | 35 | 100 | 63 | 15 | M30×1.5 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 53 |
| KR 90 PP | 1950 | KRE 90 PP | 2571 | 90 | 30 | 35 | 100 | 63 | 15 | M30×1.5 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 53 | |
| KRV 90 | 1970 | KRVE 90 | 2030 | 90 | 30 | 35 | 100 | 63 | 15 | M30×1.5 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 53 | |
| KRV 90 PP | 1970 | KRVE 90 PP | 2030 | 90 | 30 | 35 | 100 | 63 | 15 | M30×1.5 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 53 | |
| NUKR 90 | 2300 | NUKPE 90 | 2571 | 90 | 30 | 35 | 100 | 63 | 15 | M30×1.5 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 47 | |
Pictures
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Cage: | With Cage |
|---|---|
| Rows Number: | Single |
| Load Direction: | Radial Bearing |
| Style: | With Outer Ring |
| Material: | Bearing Steel |
| Type: | Closed |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
How does proper installation and alignment impact the performance and longevity of track bearings?
Proper installation and alignment play a critical role in the performance and longevity of track bearings. Correct installation ensures that the bearings are positioned and secured accurately, while proper alignment ensures that the load is distributed evenly and the bearings operate smoothly. Here’s an explanation of how proper installation and alignment impact the performance and longevity of track bearings:
Installation Impact:
- Load Distribution: Proper installation ensures that the track bearings are aligned and positioned correctly, allowing for even load distribution. When bearings are installed incorrectly, the load may be unevenly distributed, leading to excessive wear on certain parts of the bearings and reduced overall performance.
- Stability and Rigidity: Accurate installation provides stability and rigidity to the track bearings. Properly secured bearings minimize the risk of movement or vibration during operation, which can cause additional stress, premature wear, and potential damage to the bearings and surrounding components.
- Reduction of Misalignment: Correct installation minimizes the chances of misalignment between the track bearings and the track or guide rails. Misalignment can lead to uneven loading, increased friction, and accelerated wear and tear on the bearings. Proper alignment reduces these issues, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
- Prevention of Contamination: During installation, it is important to take precautions to prevent contamination of the track bearings. Proper handling techniques, cleanliness, and the use of appropriate tools or protective measures help avoid introducing dirt, dust, or debris that can compromise the bearing’s performance and longevity.
Alignment Impact:
- Reduced Friction and Wear: Proper alignment of track bearings helps minimize friction and wear. When bearings are misaligned, excessive forces and irregular motion can occur, leading to increased friction and accelerated wear. Proper alignment ensures that the bearings operate within their intended design parameters, reducing friction and promoting longevity.
- Optimal Load Distribution: Correct alignment ensures that the load is distributed evenly across the track bearings. This prevents excessive stress on specific areas of the bearings, reducing the risk of premature failure and extending their service life. Optimal load distribution also contributes to smoother operation and improved overall performance.
- Minimized Noise and Vibration: Proper alignment helps minimize noise and vibration during operation. Misaligned track bearings can result in irregular motion, leading to unwanted noise and vibration that can affect the performance, comfort, and efficiency of the machinery or equipment. Proper alignment promotes smoother and quieter operation.
- Improved Efficiency: When track bearings are correctly aligned, the machinery or equipment experiences reduced resistance and improved efficiency. Misalignment can result in energy losses, increased power consumption, and decreased overall efficiency. Proper alignment ensures optimal power transfer and minimizes energy wastage.
It is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the specific track bearings being installed. Proper installation techniques, including accurate positioning, secure fastening, and appropriate alignment, contribute to the optimal performance, reliability, and longevity of track bearings in various applications.

How do track bearings contribute to the precision, accuracy, and reliability of motion control systems?
Track bearings play a crucial role in enhancing the precision, accuracy, and reliability of motion control systems. They provide several key contributions that ensure smooth and consistent linear motion. Here’s a detailed explanation:
- Precision Guidance: Track bearings offer precise guidance for linear motion systems. They are designed with close tolerances and accurate geometries, allowing for accurate positioning and control of the moving components. This precision guidance ensures that the desired motion is achieved with minimal deviation or error.
- Smooth and Consistent Motion: By minimizing friction and providing smooth rolling or sliding surfaces, track bearings enable smooth and consistent motion in motion control systems. They reduce the effects of irregularities, misalignments, or vibrations, resulting in smoother operation and improved accuracy.
- Repeatable Performance: Track bearings provide repeatable performance in motion control systems. They offer consistent and predictable motion characteristics, allowing for precise and repeatable positioning of the moving components. This repeatability is essential in applications that require high accuracy and consistency, such as CNC machining, semiconductor manufacturing, and precision measurement systems.
- Load Distribution: Track bearings distribute the load evenly along their length, helping to minimize stress concentrations on specific components. This even load distribution improves the overall stability and reliability of the motion control system. It reduces the risk of component failure, deformation, or excessive wear, contributing to enhanced system reliability.
- Minimized Play and Backlash: Track bearings are designed to minimize play and backlash, which are undesirable movements or clearances between components. Play and backlash can introduce inaccuracies and reduce the precision of motion control systems. Track bearings with tight tolerances and optimized designs help minimize these undesirable effects, ensuring precise and accurate motion.
- Stiffness and Rigidity: Track bearings provide stiffness and rigidity to the motion control system. They resist deflection and maintain their shape under load, minimizing any unwanted flexing or bending. This stiffness enhances the overall stability and precision of the system, allowing for precise control and accurate motion even under varying loads or external forces.
- Resistance to Contamination: Track bearings are often equipped with seals or shields to protect against contaminants such as dirt, dust, or liquids. This protection helps maintain the precision and reliability of the motion control system by preventing the ingress of particles that could interfere with the smooth operation of the bearings or cause premature wear and failure.
By incorporating track bearings into motion control systems, industries can benefit from improved precision, accuracy, and reliability. Whether it’s achieving precise positioning, ensuring consistent and repeatable motion, minimizing play and backlash, or providing reliable load distribution, track bearings contribute to the overall performance and integrity of motion control systems.
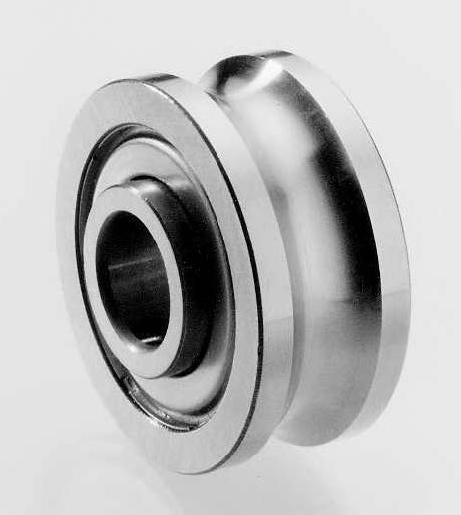

What are track bearings, and how are they used in various applications?
Track bearings, also known as track rollers or track follower bearings, are specialized rolling bearings designed to operate in track-based systems. They are used in various applications that require guided linear or rotational motion. Let’s explore in detail the characteristics of track bearings and their common applications:
- Design and Construction: Track bearings typically consist of an outer ring, an inner ring, a set of rolling elements (such as rollers or needles), and a cage that holds the rolling elements together. The outer ring features a track or guide surface, while the inner ring is mounted on a shaft or stud. The rolling elements facilitate smooth rolling motion along the track, allowing for linear or rotational movement.
- Guided Motion: Track bearings are primarily used to provide guided motion in applications where components need to move along a defined path or track. The outer ring’s track surface interfaces with the track or guide rail, ensuring precise and controlled motion. This guided motion is crucial in various applications such as material handling systems, conveyors, cam mechanisms, and automated machinery.
- Load Support: Track bearings are designed to support and distribute loads, both radial and axial, in track-based systems. They can handle substantial loads while maintaining smooth motion and minimizing friction. The load-carrying capacity of track bearings makes them suitable for applications involving heavy loads, such as construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and industrial automation systems.
- Multiple Types: Track bearings come in various types to suit different application requirements. Some common types include yoke type track rollers, stud type track rollers, and cam followers. Yoke type track rollers have thick outer rings and can withstand high radial loads. Stud type track rollers have a stud instead of an inner ring and are suitable for applications with limited space. Cam followers have a stud with a built-in roller and are commonly used in cam-driven systems.
- Sealing and Contamination Protection: In many applications, track bearings are exposed to harsh environments and contaminants. To ensure reliable operation, track bearings often incorporate sealing arrangements or protective coatings. These features help prevent the ingress of dust, dirt, moisture, or other contaminants, prolonging the bearing’s service life and reducing the risk of premature failure.
- Various Applications: Track bearings find applications in a wide range of industries and systems. Some common applications include:
- Material Handling Systems: Track bearings are used in conveyors, roller tracks, and overhead cranes to facilitate smooth and guided movement of materials.
- Automated Machinery: Track bearings are employed in automated machines and robotic systems for precise motion control and positioning.
- Cam Mechanisms: Track bearings are utilized in cam-driven systems, where they follow the profile of the cam and translate the rotary motion into linear or oscillating motion.
- Construction Equipment: Track bearings are found in construction machinery, such as excavators, bulldozers, and compactors, to support the tracks or guide wheels.
- Agricultural Machinery: Track bearings are used in agricultural equipment, including tractors, combines, and harvesters, to support the tracks or guide wheels and provide reliable movement.
- Printing and Packaging Machinery: Track bearings are employed in printing presses, packaging machines, and labeling systems to ensure precise and guided movement of the printing heads, packaging materials, or labels.
In summary, track bearings are specialized rolling bearings designed for guided linear or rotational motion along a track or guide rail. They provide precise motion control, support substantial loads, and find applications in various industries such as material handling, automation, construction, agriculture, printing, and packaging. With their ability to facilitate guided motion and handle significant loads, track bearings contribute to the smooth and reliable operation of track-based systems in a wide range of applications.


editor by CX 2024-05-07